Introduction
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that represents real-world entities as objects. Each object has attributes (data) and methods (actions). OOP makes your code reusable, modular, and easier to maintain.
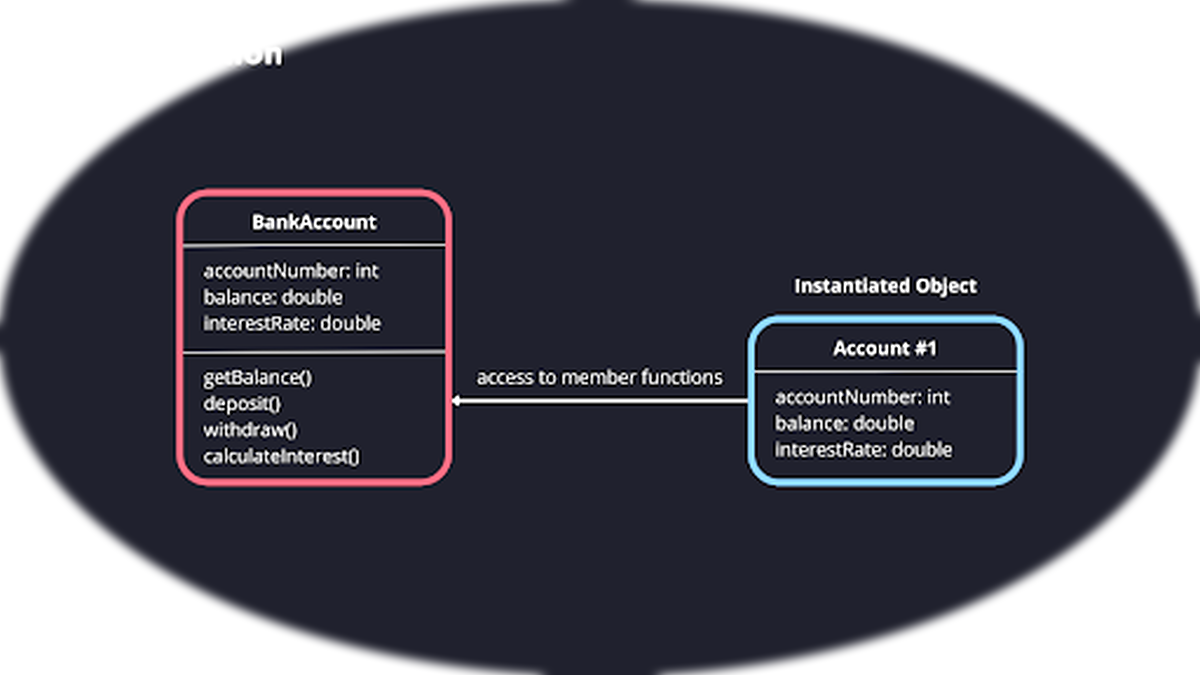 Class
Class
 Obj1
Obj1
 Obj2
Obj2
 Obj3
Obj3
- Understand why OOP is crucial for modern software development.
- Learn main concepts: Class, Object, Inheritance, Polymorphism, Encapsulation, Abstraction.
Core OOP Concepts
Class
A class is a blueprint for creating objects. It defines attributes and methods that the objects will have.
Object
An object is an instance of a class with its own unique data and behavior.
Inheritance
Inheritance allows a class (child) to inherit properties and methods from another class (parent), promoting code reuse.
Polymorphism
Polymorphism allows the same method to behave differently in different classes or contexts, making programs more flexible and extensible.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation hides the internal details of an object and exposes only what is necessary, improving security and reducing complexity.
Abstraction
Abstraction focuses on essential features while ignoring irrelevant details, helping manage complexity in large programs.
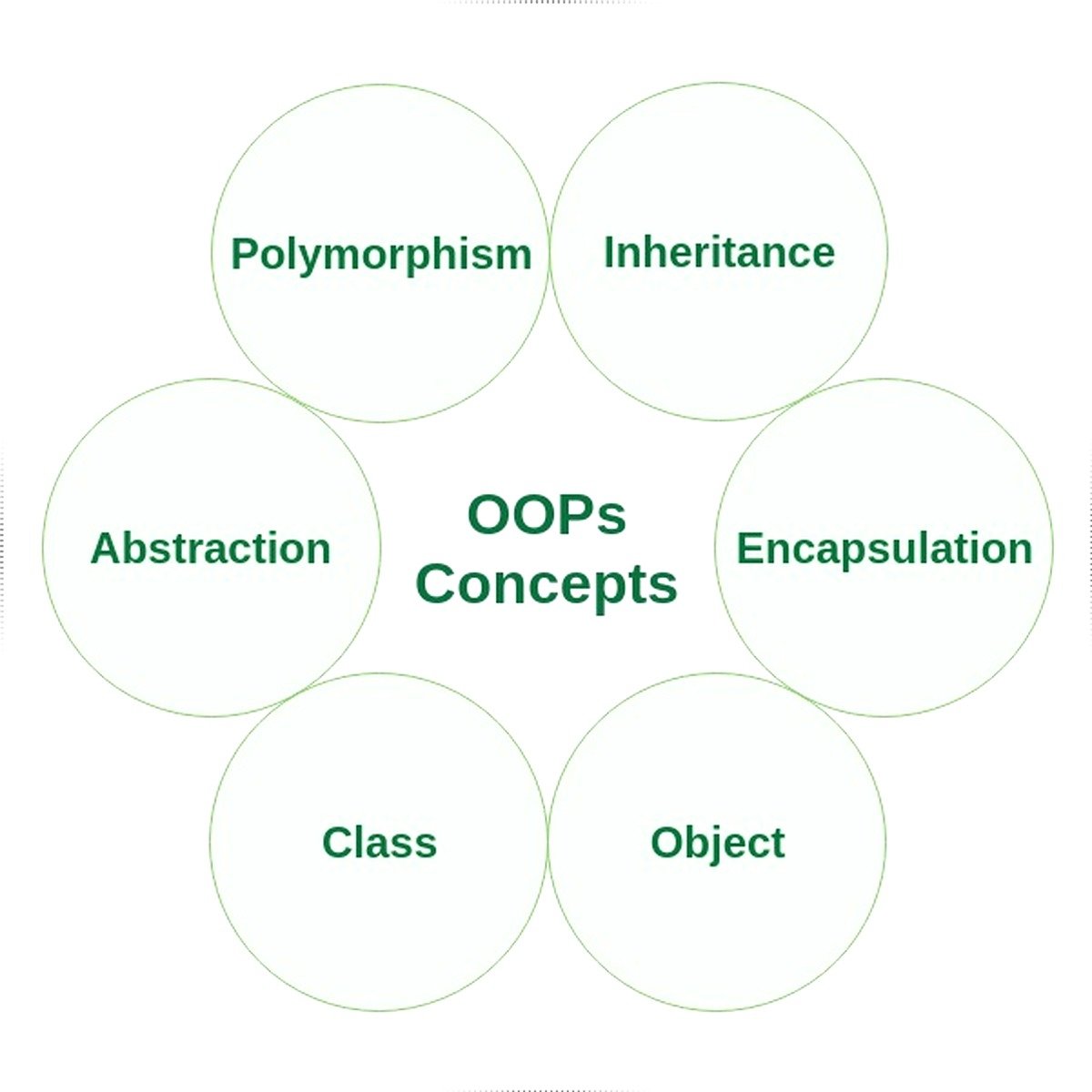
Visual Representation of Core OOP Concepts
Exercises
Practice OOP concepts by creating classes, objects, and using inheritance and polymorphism. Try building small programs to reinforce learning.
- Create a `Car` class with attributes like `model`, `color` and methods `start()` and `stop()`.
- Create a child class `ElectricCar` that overrides the `start()` method.
- Build a mini console-based project using multiple classes interacting together.
Practical Projects
Hands-on projects are the best way to master OOP. Implement small applications that use multiple classes, inheritance, and encapsulation.
- Build a simple text-based bank account system using classes and methods.
- Create a library management system using inheritance and encapsulation.
- Develop a mini-game like Tic-Tac-Toe using OOP concepts in Python or Java.
Flowchart Example for Practical OOP Project
Interactive Python & Java Demo
View and learn Python and Java code examples for OOP concepts. Toggle between languages and listen to explanations in English or Hindi.
# Python OOP Example
class Car:
def __init__(self, model, color):
self.model = model
self.color = color
def start(self):
print(f"{self.model} is starting.")
def stop(self):
print(f"{self.model} has stopped.")
class ElectricCar(Car):
def start(self):
print(f"{self.model} (Electric) is silently starting.")
mycar = ElectricCar("Tesla Model 3", "Red")
mycar.start()
mycar.stop()
Conclusion
Mastering Object-Oriented Programming is essential for writing clean, maintainable, and scalable software. Practice regularly with exercises, practical projects, and by reading and modifying code examples.