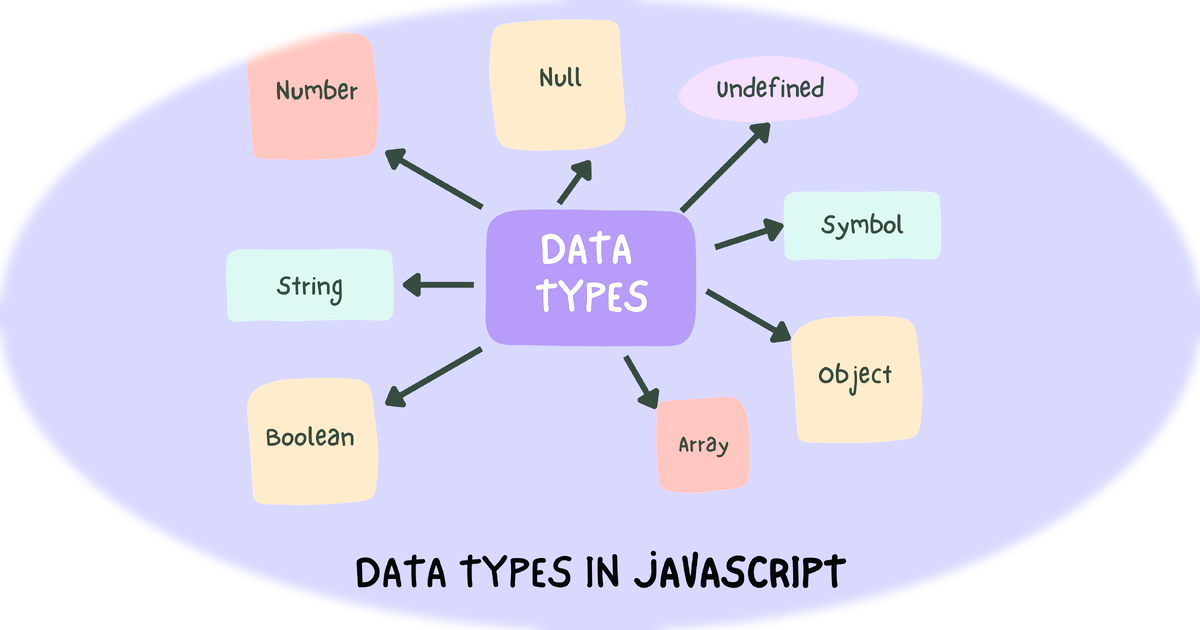
1. Variables & Data Types
Variables act like containers for storing data. Understanding types helps in writing correct programs. Numbers, Strings, and Booleans are basic data types.
Variables data store करने के लिए containers की तरह होते हैं। Types समझना सही program लिखने में मदद करता है। Numbers, Strings, और Booleans basic data types हैं।
Use let, const, var to declare variables
Assign appropriate values
Choose correct data types
let, const, var का use करेंसही value assign करें
Correct data type चुनें
Example: Store and print a number
Example: Number store करें और print करें
Run Code
Copy Code
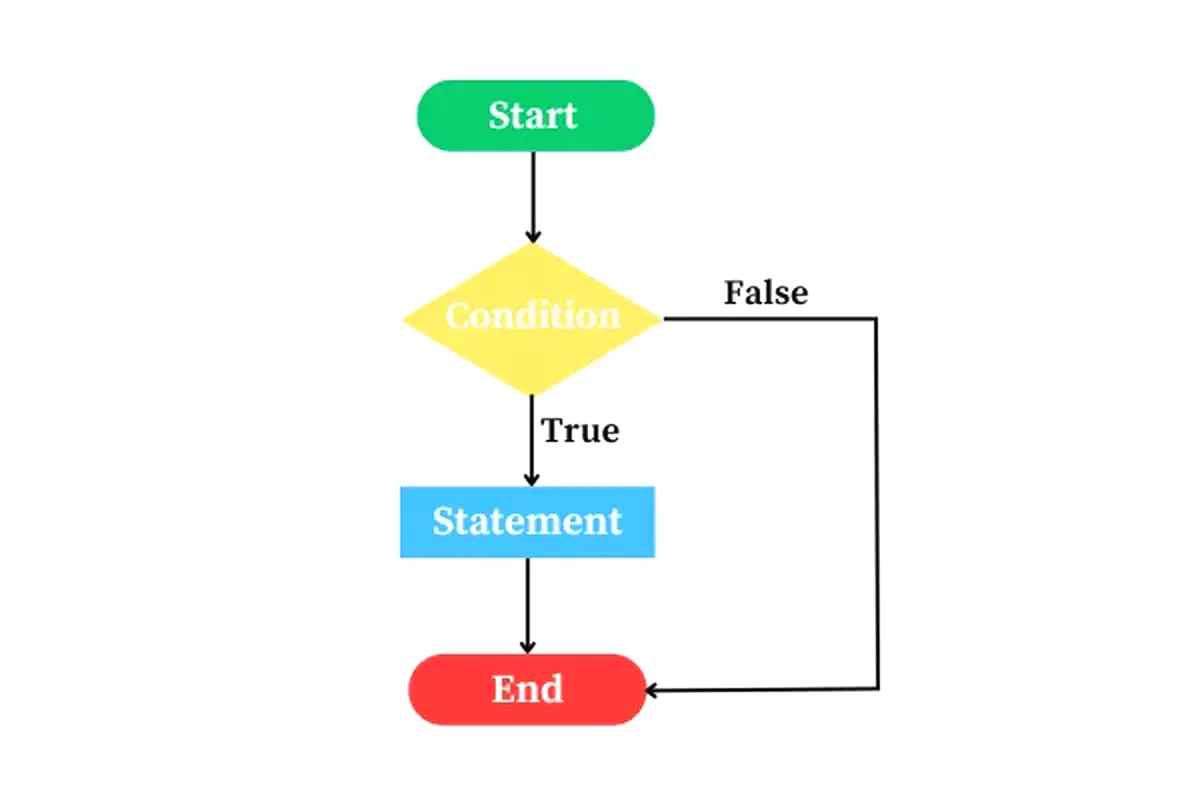
2. Conditional Statements
Conditional statements allow decision making in code. You can execute certain blocks only if a condition is true.
Conditional statements code में decision लेने में मदद करते हैं। Block तभी execute होता है जब condition true हो।
Use if, else, else if
Compare values using operators like ==, ===, >, <
if, else, else if use करेंValues compare करें ==, ===, >, < से
Example: Check age eligibility
Example: Age eligibility check करें
Run Code
Copy Code
3. Loops
Loops are used to repeat a block of code multiple times. For, While, and Do-While are the common loops in programming.
Loops एक block को बार-बार execute करने के लिए इस्तेमाल होते हैं। For, While, और Do-While common loops हैं।
Use for when number of iterations is known
Use while or do-while when condition based
जब iterations fixed हों, for use करें
Condition-based के लिए while या do-while use करें
Diagram
Example: Print numbers from 1 to 5
Example: 1 से 5 तक numbers print करें
Run Code
Copy Code
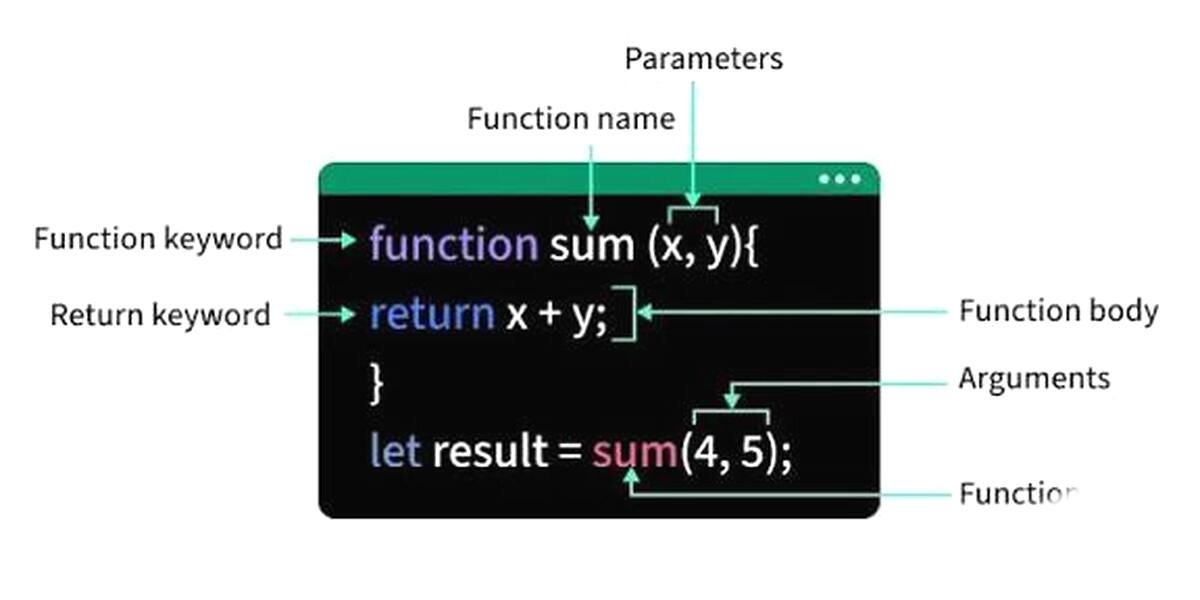
4. Functions
Functions help to organize code into reusable blocks. They take input, process, and return output.
Functions code को reusable blocks में organize करने में मदद करते हैं। यह input लेते हैं, process करते हैं और output return करते हैं।
Diagram
Example: Function to add two numbers
Example: दो numbers को add करने के लिए function
Run Code
Copy Code
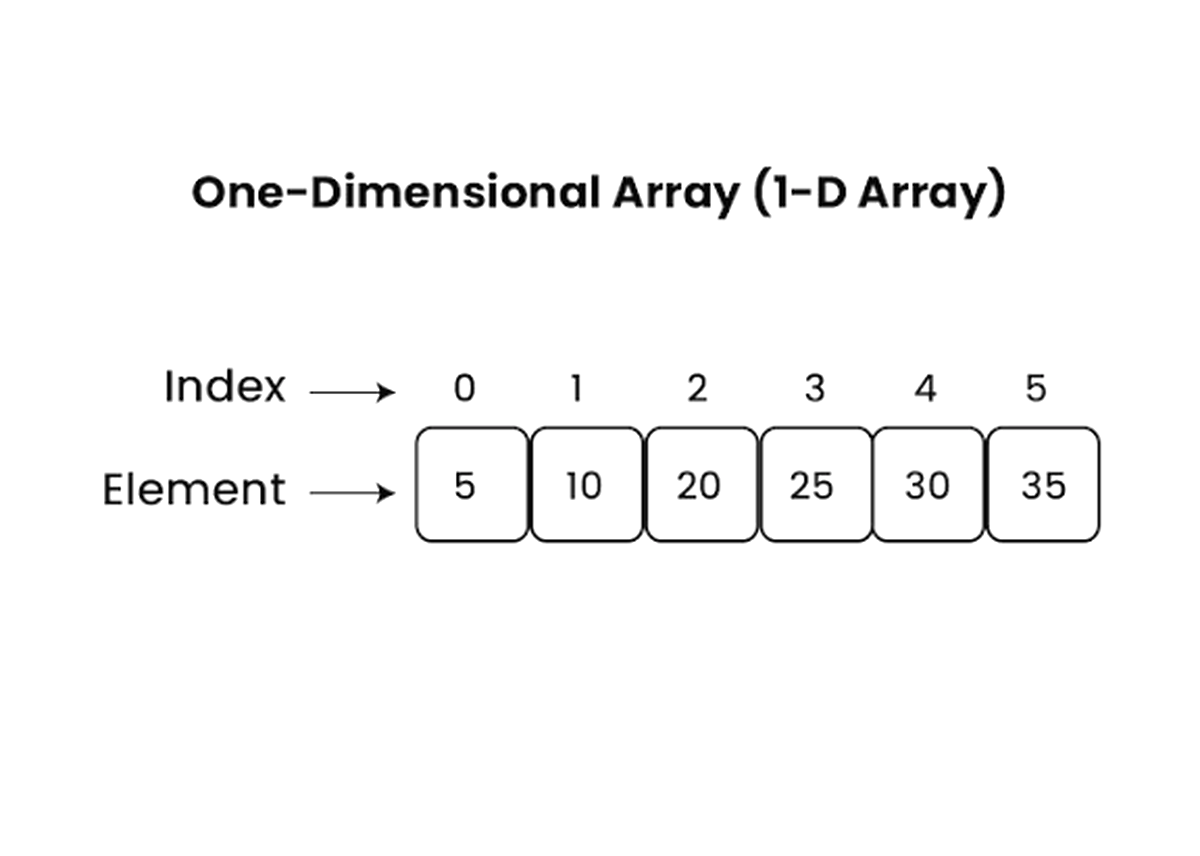
5. Arrays
Arrays store multiple values in a single variable. They are useful for managing lists and collections.
Arrays एक variable में multiple values store करने के लिए use होते हैं। यह lists और collections manage करने में helpful हैं।
Diagram
Example: Array of numbers
Example: Numbers की Array
Run Code
Copy Code
6. Objects
Objects store key-value pairs. They help represent real-world entities and their properties.
Objects key-value pairs store करते हैं। यह real-world entities और उनके properties को represent करने में मदद करता है।
Diagram
Example: Object representing a person
Example: Person represent करने वाला object
Run Code
Copy Code
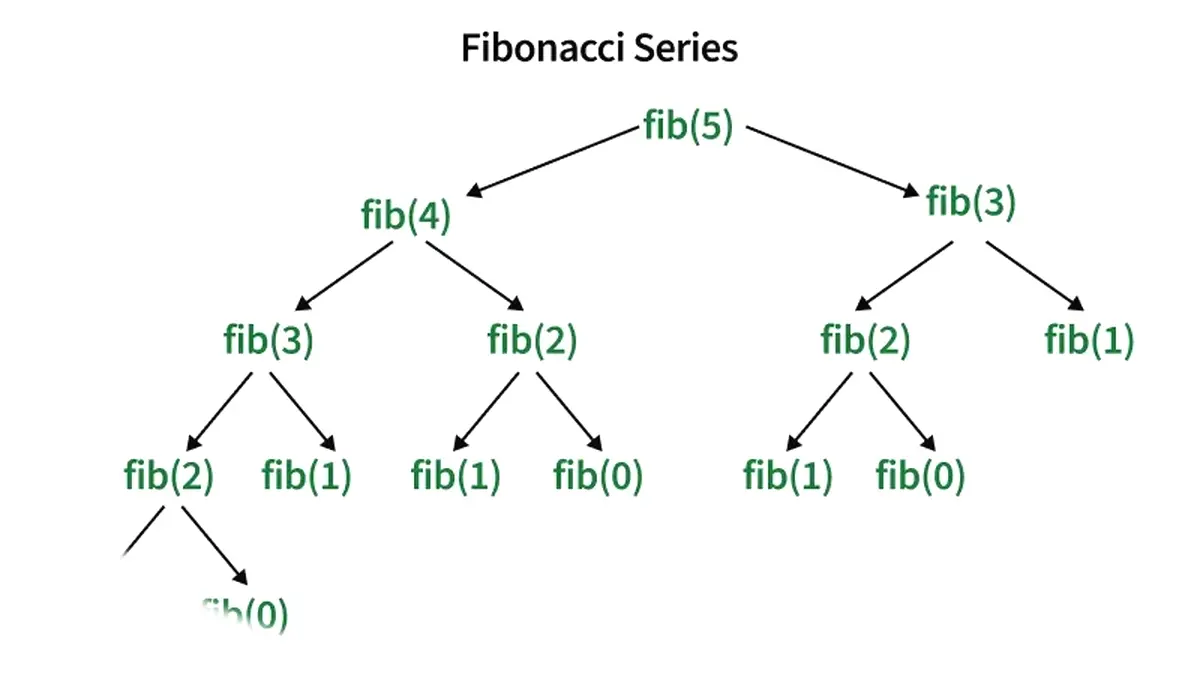
7. Recursion
Recursion is a technique where a function calls itself. Useful in solving problems like factorial or Fibonacci.
Recursion वह technique है जिसमें function खुद को call करता है। Factorial या Fibonacci problems में useful है।
Diagram
Example: Factorial using recursion
Example: Recursion से Factorial
Run Code
Copy Code
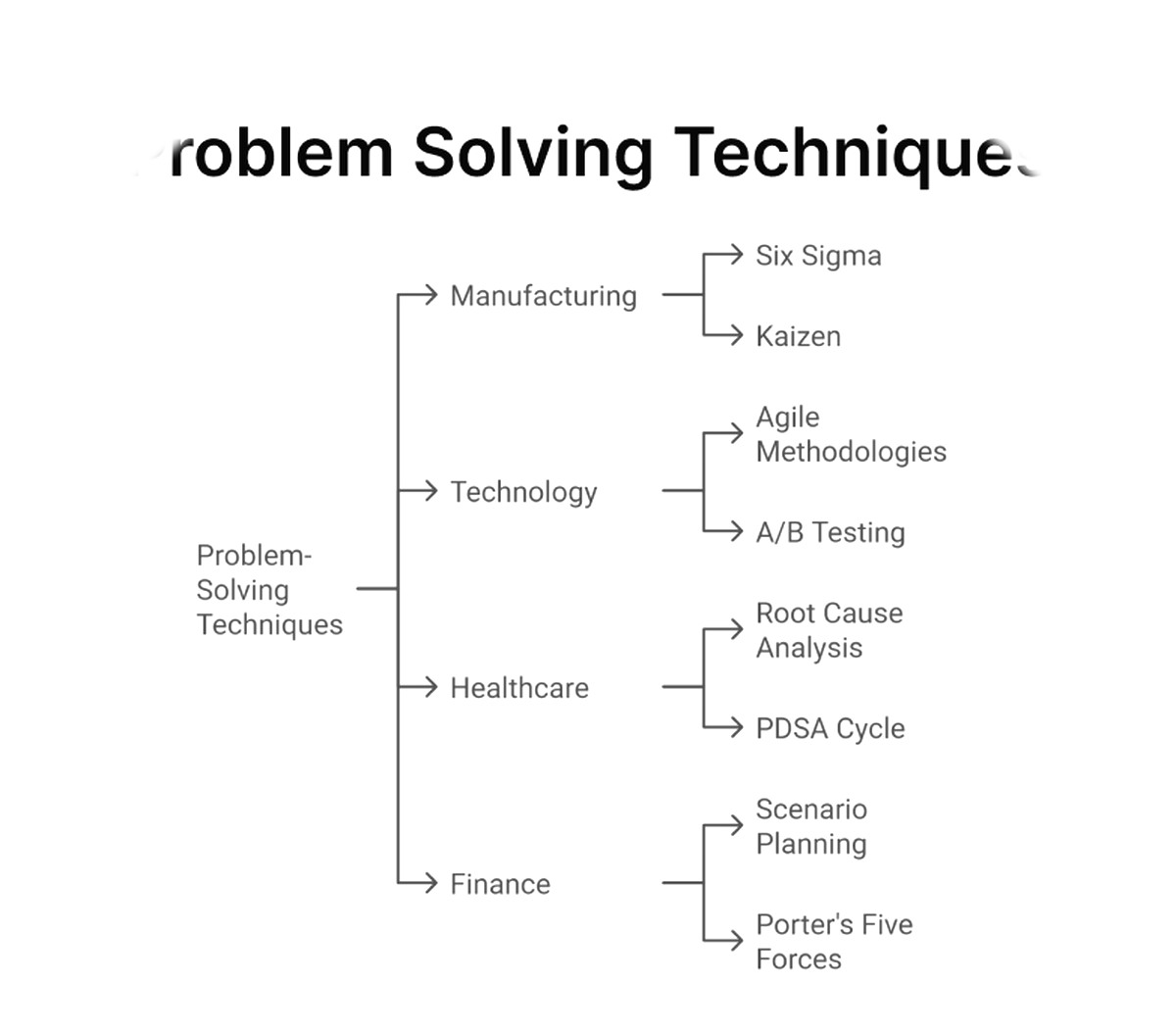
8. Problem Solving Techniques
Developing logic requires systematic problem-solving. Break problems into smaller steps and solve incrementally.
Logic develop करने के लिए systematic problem-solving जरूरी है। Problems को छोटे steps में divide करें और incrementally solve करें।
Diagram
Example: Check prime number
Example: Prime number check करें
Run Code
Copy Code
9. Mini Projects
Apply your logic skills to small projects like calculators, to-do apps, and text-based games.
Logic skills apply करने के लिए mini projects बनाएं जैसे calculators, to-do apps, text-based games।
Diagram
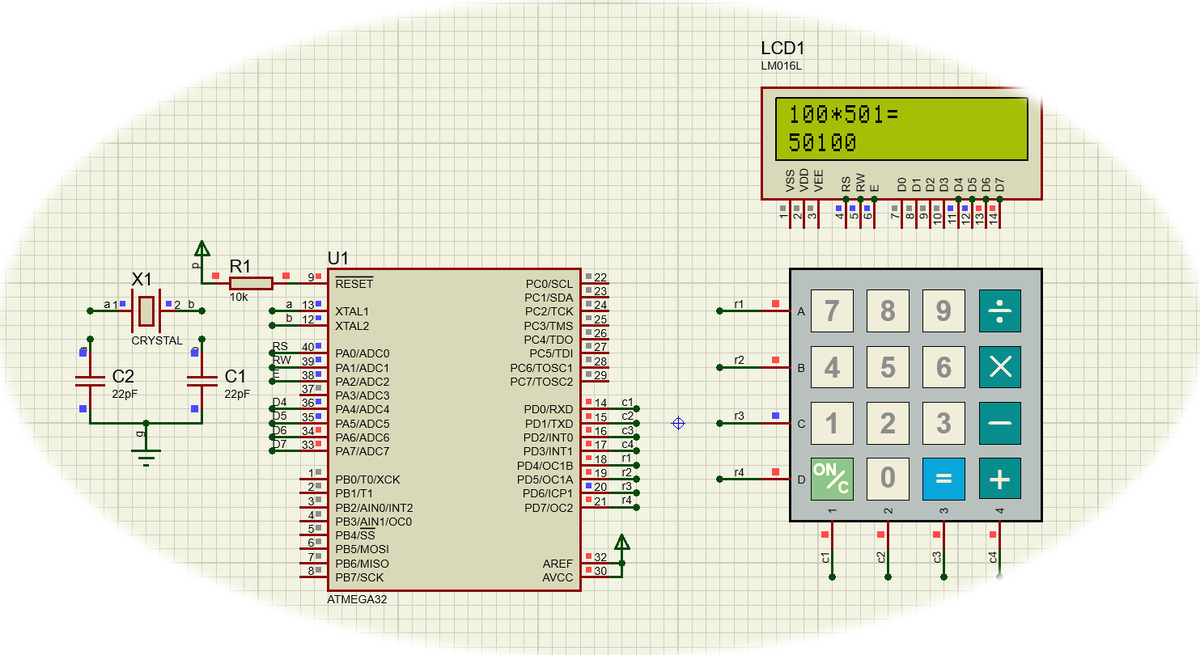
Example: Simple addition calculator
Example: Simple addition calculator
Run Code
Copy Code
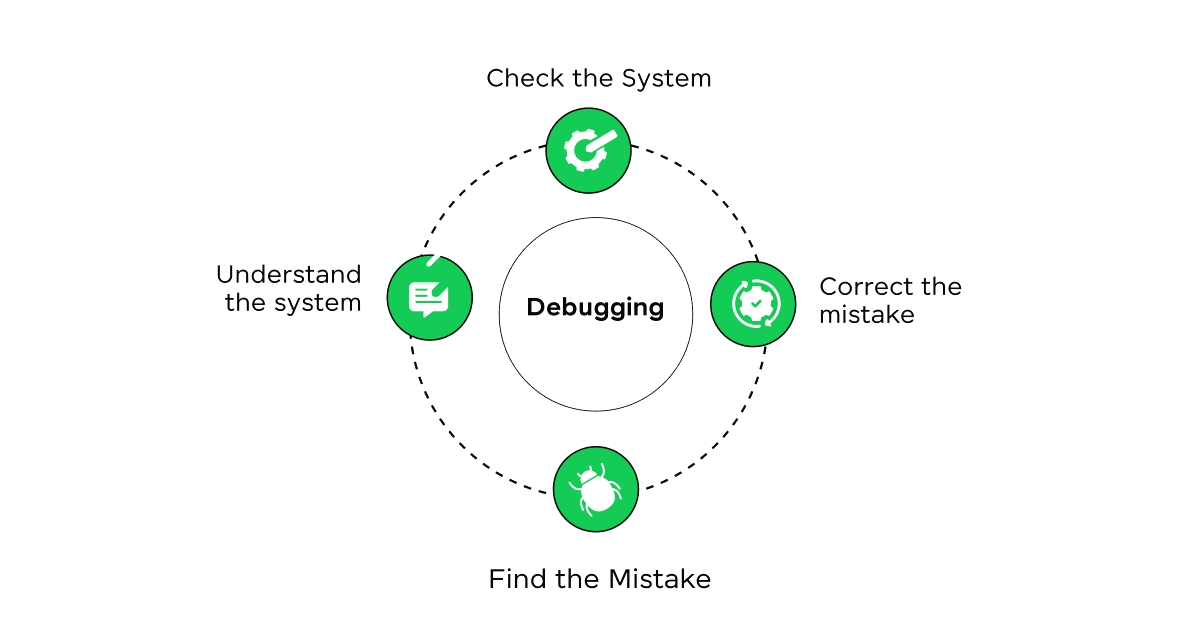
10. Debugging & Optimization
Debugging helps find and fix errors. Optimization improves code performance and efficiency.
Debugging errors find और fix करने में मदद करता है। Optimization code performance और efficiency improve करता है।
Diagram
Example: Debug a code snippet
Example: Code snippet debug करें
Run Code
Copy Code
Enjoyed this article?
Share it with your network!
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn